Hello Readers,
My name is Jan, and I'm a Sound Designer at Studio Windsocke. I'm thrilled to share some insights about our first game, Passing By – A Tailwind Journey.
Originally started as a student project, this small prototype eventually became our studio’s debut title, culminating in its release in March 2024. When we began, I had no prior experience in sound design—yet thanks to Wwise, I found a great entry point into the world of interactive audio. From day one, my goal was to create an engaging and coherent auditive atmosphere that could support the game’s charm and narrative.
In this blog article, I’d like to walk you through how I approached this challenge, how Wwise helped me shape the audio identity of the game, and what I learned along the way.

A Vibrant World Above the Clouds
Passing By – A Tailwind Journey is a whimsical and atmospheric adventure set in a vibrant world of floating islands and endless skies. Players take on the role of Curly, a young balloonist tasked with delivering a mysterious letter. Throughout the journey, you navigate your balloon ship across various biomes, solve intricate puzzles, and manage resources to survive. The game blends 2D puzzle platforming, survival, and adventure into a unique and immersive experience.
As you explore, you'll meet quirky island inhabitants and fellow travelers, each adding depth and charm to your journey. The beautiful 2D low-poly art style and dynamic, atmospheric soundtrack enhance the enchanting experience. Whether customizing your ship or uncovering ancient secrets, every moment in Passing By – A Tailwind Journey is designed to be memorable and engaging.
From University Project to Published Game
Passing By began as a student project at the University of Bayreuth. In September 2020, our team released an initial prototype on itch.io, considering it a completed academic project at the time. To our delight, the game received very positive feedback, which encouraged us to keep tinkering with it—even releasing a few small updates afterward.
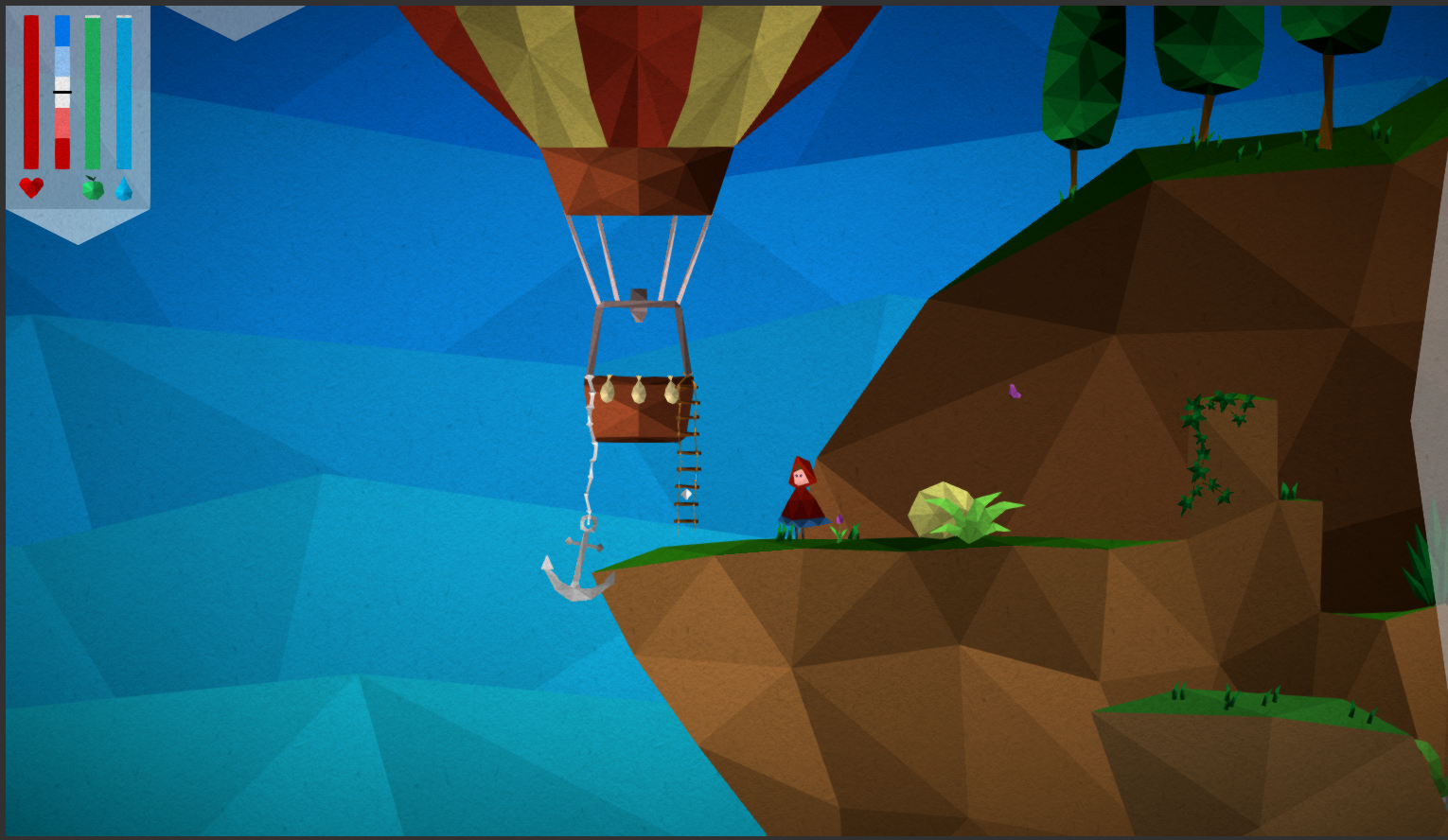
Prototype version
Then, in 2021, we received unexpected recognition in the form of two major newcomer awards in Germany. These accolades, along with the encouraging community response, reignited our passion for the game and motivated us to pursue further development.

Our breakthrough came at gamescom 2022, where we connected with Dear Villagers, who later became our publisher. This partnership transformed our university project into a full-fledged commercial venture. With renewed energy, we dedicated ourselves to perfecting the game, preparing for its official release in March 2024.
This journey—from prototype to published title—was filled with challenges, surprises, and learning moments. It marked not only our studio’s debut but also my own first real steps into the world of sound design.
Choosing Wwise & Getting Started
Like many student teams, we didn’t have expertise in every discipline—sound design being one of them. Our decision to use Wwise came through our composer, Michi, who was also my roommate at the time. A friend recommended Wwise for its capabilities with interactive music, and Michi was eager to compose a dynamic game soundtrack, so the choice was clear.
Living with Michi allowed for seamless collaboration, and I was excited to dive into new software and creative territory. That’s how I stepped into the role of the game’s sound designer.
To begin, I worked through the Wwise Certification Courses—especially the Fundamentals and Unity Integration modules. I started small: footsteps for Curly, ambient wind, and a few interaction sounds. While working with an external sound engine sometimes added integration challenges, I was impressed by how accessible Wwise was from the beginning.
Structuring the Audio Workflow
After the initial experiments with Wwise, I created an audio asset list for the project and shared it with the team. Everyone was invited to contribute ideas for the sounds needed in their levels. Over time, this list became a vital production tool and was revised multiple times as the game evolved.
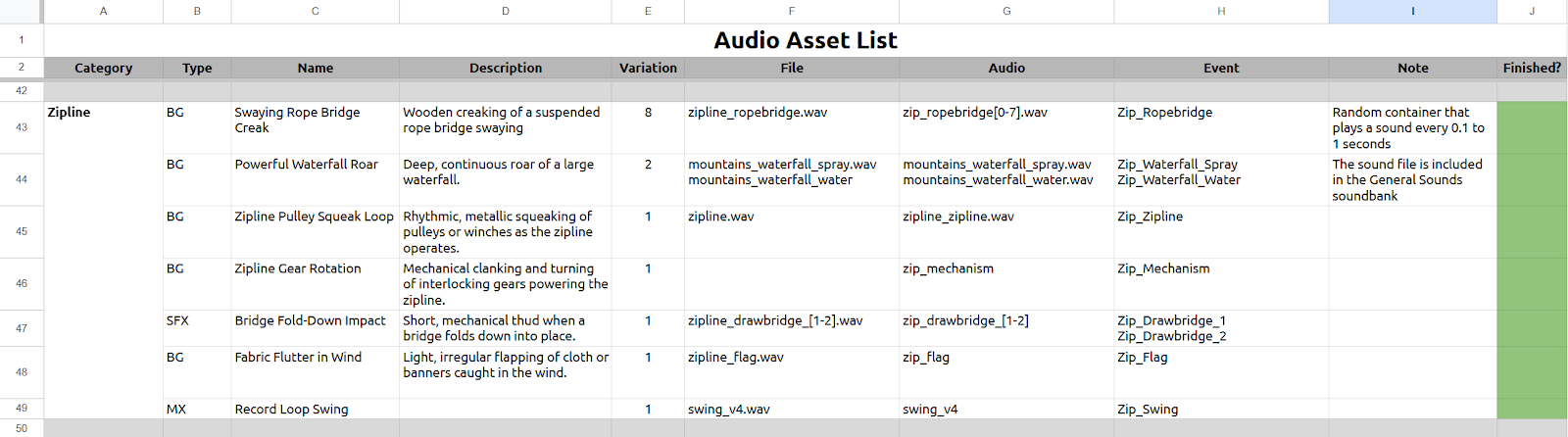
In the list, I also distinguished between the names of the sounds and their corresponding Wwise events. This helped maintain clarity, especially when sounds were reused across multiple events. Additionally, a dedicated comment column allowed me to document more complex sound setups for better traceability. Since I was the only sound designer on the team, the audio asset list initially served as a communication tool but quickly became a working document. It gave me a clear overview of the sound design process and helped me track my progress efficiently throughout development.
Working Without a Studio (And Still Making It Work)
Since I didn’t have access to recording equipment or a studio, I turned to online resources like freesound.org, exclusively using CC0 (public domain) sounds. With these resources, I initially relied on Audacity to edit and tailor the sounds to fit my vision for the game. However, it also proved extremely helpful that Wwise itself allows for sound editing and the application of effects. In many cases, this made the detour through external tools unnecessary and enabled a more seamless integration of the sounds into the engine.
As the project progressed, my skills and confidence as a sound designer grew alongside it. In the beginning, I searched for sounds that already matched my needs as closely as possible—ideally requiring only minor tweaks like pitch shifts. Later, I became more comfortable layering and combining different sounds to achieve the desired effect. So in this sense, Passing By – A Tailwind Journey was not only our first release as a studio, but also my personal learning journey into sound design.
One particularly helpful habit throughout the process was flagging difficult or unsolved sound challenges in my audio asset list. This allowed me to return to them at a later stage, often with new ideas or improved skills, and eventually find suitable solutions.
Optimizing SoundBanks for a Floating World
As optimization was a key focus in our academic background, I started collaborating early with our programmer, Marius, to structure an efficient SoundBank system. While it evolved slightly over time, the basic structure followed the geography of our game world:
Passing By – A Tailwind Journey takes place across floating islands grouped into five biomes: Polar, Mountains, Meadows, Beach, and Volcanic. Each biome received its own dedicated SoundBank, containing all audio assets shared across the smaller islands in that region. For example, the Beach biome features ambient sounds like seagulls and ocean waves, while the Volcanic biome includes bubbling lava and distant eruptions. The Meadows biome, on the other hand, is characterized by birdsong and the soft buzzing of bees—natural sounds you'd expect to hear in a tranquil grassland setting. In addition to these, larger story islands were given their own SoundBanks to account for their unique soundscapes and interactive elements. We also created a General Sounds SoundBank, containing assets that needed to be permanently loaded, such as UI sounds, footsteps, and balloon ship audio.
At runtime, only the General Sounds SoundBank remains constantly loaded. Biome-specific SoundBanks are loaded dynamically when the player lands on an island within that biome and unloaded after departure. If a player lands on a story island, its dedicated SoundBank is loaded in parallel.
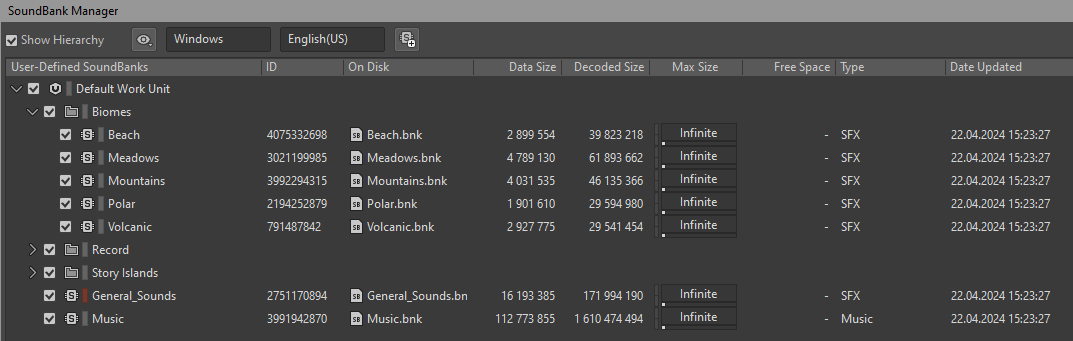
Although we sometimes had to duplicate sounds—like waterfalls appearing in several biomes—we tried to keep redundancies to a minimum. The final setup also included two separate banks for our interactive soundtrack and intradiegetic music.
This modular approach helped us manage memory efficiently without compromising audio richness—especially important when optimizing the game for platforms like the Nintendo Switch. Planning this structure early on paid off greatly in the long run.
Reflections and Takeaways
Looking back, working on Passing By – A Tailwind Journey was not only my first deep dive into sound design but also an incredibly formative experience. From those early days of experimenting with footsteps in Wwise to shaping entire ambiences across multiple biomes, I gradually found my creative voice. More than once, I had to overcome uncertainty, find practical solutions, and learn by doing, failing, and iterating.
Thanks to the modularity and flexibility of Wwise, I was able to grow alongside the project—adding increasingly complex sound variations, effects, and game syncs as my skills evolved. This experience taught me that you don’t need to be a fully trained sound designer with expensive gear or a professional Foley studio. Tools like Wwise empower you to create sophisticated audio experiences with just a computer and a willingness to learn.
More importantly, I came to understand that good sound design isn’t about the tools alone—it’s about listening closely, working iteratively, and identifying what a scene or interaction truly needs. It’s about storytelling through sound.
I hope this article offered some insight into the world behind the audio curtain of our game. If you're starting out with interactive audio or tackling your first project—don’t be afraid to begin small. With the right tools and a curious mindset, you might be surprised by how far you can go.
Thanks for reading and happy creating!



댓글