Game jams, as fun as they can be, can be stressful and frustrating from an audio point of view. Sound integration will more than likely arrive very late in the process, and iteration and debugging time will be reduced to almost nothing. While the use of Wwise may seem like overkill, and while the development team could be afraid of adding an additional tool into the process, on the contrary, I think using Wwise is the best way to create a compelling interactive audio experience in such a short period of time. From personal experience, and from discussions I have had with other sound designers, I think arguments for choosing to use Wwise for big projects are the same and may even be more justifiable for game jams and short projects. Smooth integration in game engines, having more features available to you than standard game engine tools, and unburdening programmers from sound integration, the list of benefits can go on. So, below, I have provided a list of simple tips and tricks that will allow you to enjoy your experience during game jams or shorter projects and allow you to get the best results using Wwise.
Preparation
The last thing you want in a game jam is shady error messages, or your game not building properly. It's easier to spot any major issues from the comfort of your home rather than in the middle of a sleep-deprived crowd of people twenty minutes before deadline! So, take an hour or two before the event to prepare. It could save you a lot of stress and enable you to go there with a fair amount of technical confidence, allowing you to fully focus on having fun and creating cool sounds.
You can start by testing that the integration of the Wwise version you will be using is working well with the exact version of the game engine your team will be using. Create an empty project and try to play a sound in the editor. For game jams, chances are you won't know beforehand which platform you will be developing for, but take the time to make a build for PC, Android, and iOS. While this testing may be obvious or easy for you, in short development timeframes, it is essential that you avoid any possible technical difficulties.
Next, you should not assume that a programmer is going to help you with the actual integration. Prepare yourself to do everything on your own. Doing some quick homework and testing the integration of basic Wwise features is good practice, especially if your team will be using a game engine that you are not that familiar with or haven't used in a long time. Some features you will more than likely need and should prepare:
- Post events for different conditions : on start / on destroy / in animations / on trigger enter and exit / custom triggers / ...
- Reverb zones
- Set States and Switches
- Set RTPCs
- UI sounds (on select / on click / on pointer enter / ...)
- Prepare Attenuation curves in the units of measurement of the game engine, as well as Conversion Settings for different platforms
Again, feeling comfortable with the implementation of those features will provide you and your team with confidence and enable you to focus on your sound design.
Jamming
The big day has arrived, you are all geared up, caffeine-packed, and ready to rock. Once you have set up the source control with the programmer and pushed the Wwise integration, test a build on the programmer's machine to check everything is going well. Once again, we don't want any last-minute surprises.
After an intense brainstorming, you and your team came up with an amazing game idea. Before jumping on your recorder to start creating assets, sit down in front of Wwise for a bit. In a game jam, we are looking for simplicity and efficiency. Examine how Wwise features can help you with that.
What I like to do at game jams, and even on more traditional projects, is to create empty core Events corresponding to major changes in the game, such as :
- Character leveling up
- Weather changing
- Enemy life down to 25%
- Player death and respawn
- ....
An Event can contain all types of Actions: one shot sound, State changes, Set RTPCs, start/stop loops, control interactive music. Take a generic list of possible core Events that could contain all these Actions:
- Start_Game
- Launch_New_Game
- Start_Phase_2
- Start_Phase_3
- End_Game_Success
- Eng_Game_Defeat
- Player_Death
- Player_Respawn
Besides providing you with a good preview of a typical playthrough, having this list from the beginning will help minimize the Events count. Hence, a simpler integration afterwards. This list of Actions, combined with the use of Delay and transition time for States, should cover most of the ambiances and music behaviours you would need for a game made during a game jam.
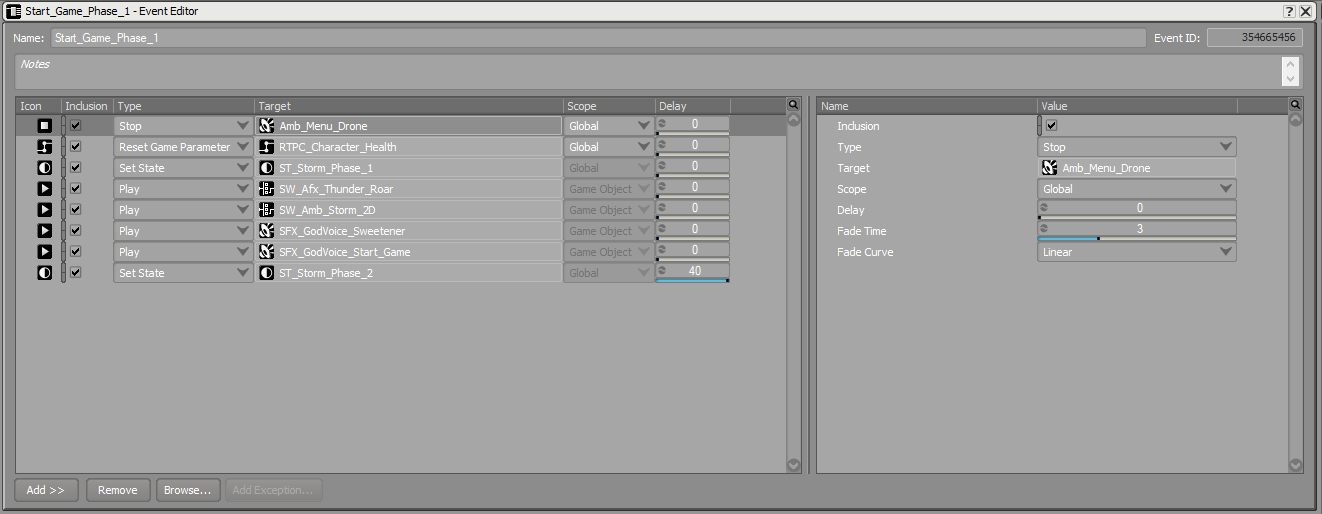
Typical example of nested Actions in an Event.
Wwise 2018.1 will also have a native Time RTPC. For games based on a timer (pretty common in game jams), you could have the entire playthrough controlled from a single Event.
In addition to organized nesting, here is a list of simple Wwise features that can be helpful for minimizing and simplifying the integration:
- States can control a lot of parameters. I tend to use those instead of RTPCs as much as possible because they are easier to use and to implement.
- RTPCs can control Switches. This is very useful when creating complex interactive systems with fewer calls from the engine.
- The 2D Panner or User-Defined 3D Paths can spatialize scripted game objects. This will allow you to control the movement and location of a particular sound before its integration and minimize bugs.
- Reverbs can be baked and User-Defined auxiliary sends can be used. When possible, make use of these because chances are that a game made in a weekend will not need a lot of different reverbs, and so everything that can be prepared and controlled in Wwise should be.
Make it sound good
The Soundcaster is a great tool in a game jam environment. There is no need to wait for any integration to be done to have a great sounding mix (hence the choice of User-Defined positions and auxiliary sends when possible)! You can simulate an entire playthrough of the game by using the core Events you created and by mixing the game. This way, you can set up your ducking system, fine-tune your RTPC's curves, and deliver fully functional and mixed SoundBanks, ready for implementation.
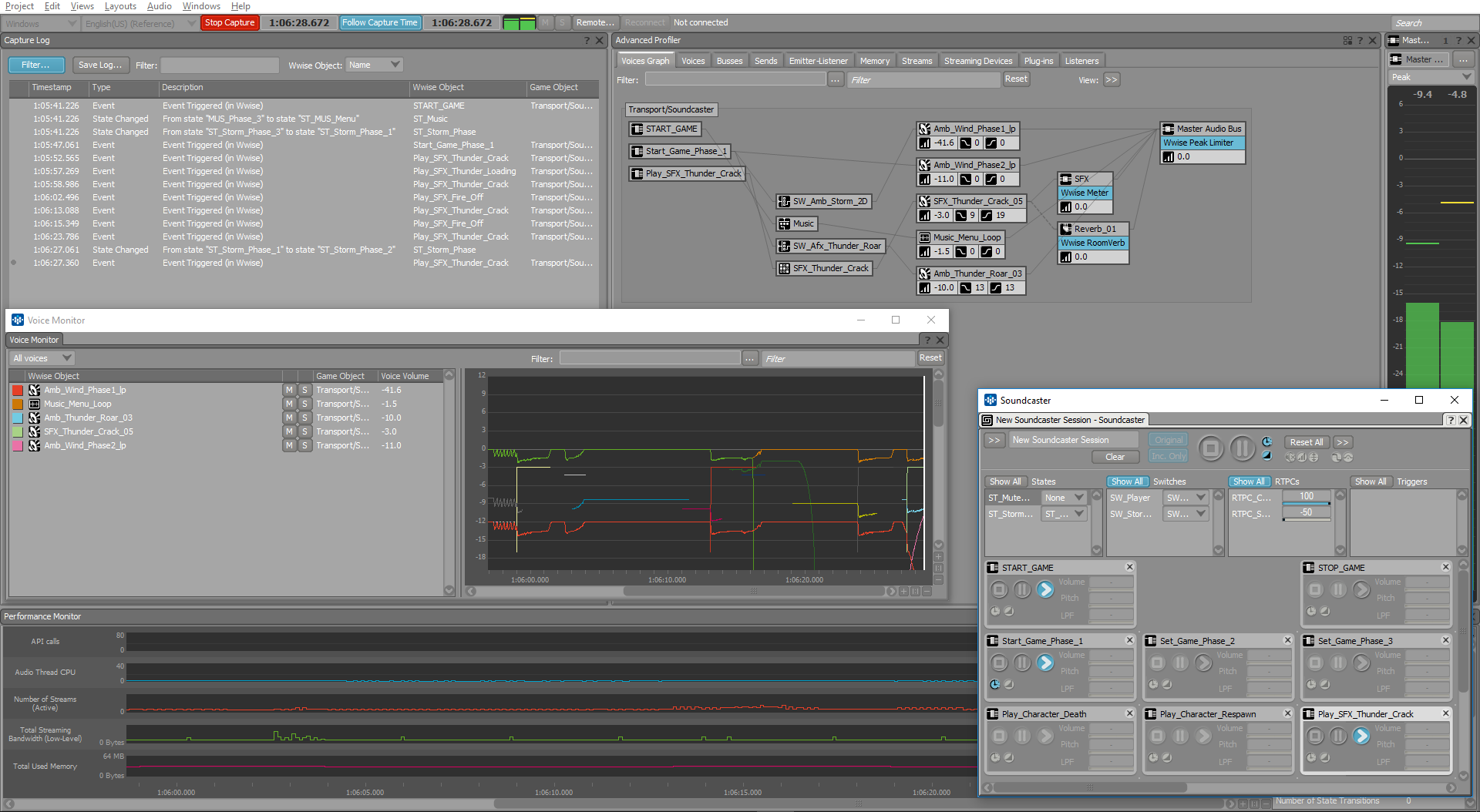
Soundcaster / Voice Monitor and Advanced Profiler are useful tools to simulate complete playthrough without having to integrate anything in the game engine.
When you are able to integrate your sound design (which may be in the last few hours of the jam...), all your homework and good practice during the jam will hopefully make the integration fast, smooth, and painless!
Conclusion
Game jams are great events for having fun with like-minded people while creating cool sounds. I always learn and improve during those events, and they sometimes give me ideas for design and integration processes for other projects. But, in essence, game audio is not the perfect fit for such a short production period since there is a high dependency on the team progress to design and integrate sounds. Therefore, complex interactive audio behaviours and a perfect sounding mix are not the easiest to achieve. From Soundcaster and nesting Events, to time-based and user-defined control of parameters, Wwise precisely offers various features that can help a sound designer work efficiently, regardless how the game production is progressing.
Game jams are also the opportunity to demonstrate all the benefits of such tools to programmers who may have never worked with audio middleware. This is a good thing for the game audio community! I would encourage students and more experienced sound designers to use Wwise for game jams, or other micro-projects.


댓글