Wwise SDK 2021.1.14
Raytracing Engine Geometry Guide
|
Wwise SDK 2021.1.14
|
Introduction
Raytracing is a technique for efficiently evaluating nth-order reflection and diffraction. 기본 개념은 리스너로부터 랜덤으로 레이를 캐스팅해 일련의 반사와 회절 경로를 따라가는 것입니다. 이 기술은 그래픽 렌더링 기술에서 영감을 받았습니다. 현재 구현 방식은 리스너와 이미터 측에서 4차 반사와 회절까지 지원합니다.

Concepts
- 주요 레이 (primary ray): 리스너로부터 직접 캐스팅되는 레이
- 반사 (reflection): 사운드가 표면에 부딪혀 나오는 것
- 회절 (diffraction): 사운드가 물체를 돌아 굽어지는 것
- 경로 (path): 리스너에서 이미터까지 이어지는 일련의 반사/회절
- 이미터 수신기 (emitter receptor): 이미터를 중심에 둔 바운딩 상자나 바운딩 구체
Settings
- 주요 레이 (primary ray) 개수 (uNumberOfPrimaryRays): 리스너로부터 캐스팅되는 레이의 개수 주요 레이의 개수를 늘리면 결과물의 퀄리티는 좋아지지만 CPU 사용률이 높아집니다. 설정된 기본 값은 대부분의 애플리케이션에 적합합니다.
- 최대 반사 차수 (maximum reflection order) (uMaxReflectionOrder): 표면에 성공적으로 부딪혀 나오는 레이의 최대 숫자 반사의 최대 차수를 높이면 더 섬세한 음향 시뮬레이션을 만들 수 있지만 CPU 성능에 큰 영향을 끼칩니다.
- Direct Diffraction Path (bEnableGeometricDiffractionAndTransmission): A direct diffraction path between the listener and an emitter is a path composed exclusively of diffraction segments. 직접 회절 경로 계산을 활성화하면 CPU 비용을 급격하게 증가시킵니다.
- 반사에 대한 회절 (bEnableDiffractionOnReflection): 반사 경로(반사 구간으로만 구성된 경로)의 시작과 끝에 회절을 활성화합니다. 반사에 대한 회절을 활성화하면 이미터나 리스너가 장애물 뒤로 이동했을 때 시뮬레이션 도중 예기치 않게 반사가 중단되는 현상을 방지합니다. 직접 회절 경로와 마찬가지로 이 도한 CPU 비용을 크게 증가시킵니다.
- 최대 경로 길이 (fMaxPathLength): 경로 구간의 최대 길이 높은 값일수록 더 긴 경로를 계산하지만 CPU 비용을 증가시킵니다.
- CPU Limit Mode (bEnableCPULimitMode): If enabled, the raytracing engine automatically limits the number of primary rays to ensure CPU usage remains around the CPU Limit Percentage.
- CPU Limit Percentage (fCPULimitPercentage): The target percentage (expressed as a percentage of an audio frame) used by the raytracing engine to compute reflections and diffractions.
CPU Limit Mode
Tweaking the number of primary rays can be tricky as it depends on the complexity of the scene (number of triangles, number of diffraction edges...) and the number of emitters. When CPU Limit Mode is active, the raytracing engine automatically adapts the number of primary rays to ensure CPU usage remains around the target value defined by the user. Although this mode minimizes peaks in CPU usage it cannot completely remove short and sudden peaks. Setting a high target value increases quality (number of reflection and diffraction paths found) at the cost of performance. While setting a low target value increases performance at the cost of quality. When CPU Limit Mode is active, the number of primary rays is capped at 500. When the number of primary rays drops down to 0, the raytracing engine stops scanning the environment. However the existing sound propagation paths are still validated and updated. As a consequence, the raytracing engine still consumes CPU. Note that the CPU Limit Mode has no effect on portal ray tracing.
Limitations
There are a few limitations when defining geometries for the raytracing engine. 이 한계에는 결과물의 성능과 품질이 모두 고려되었습니다.
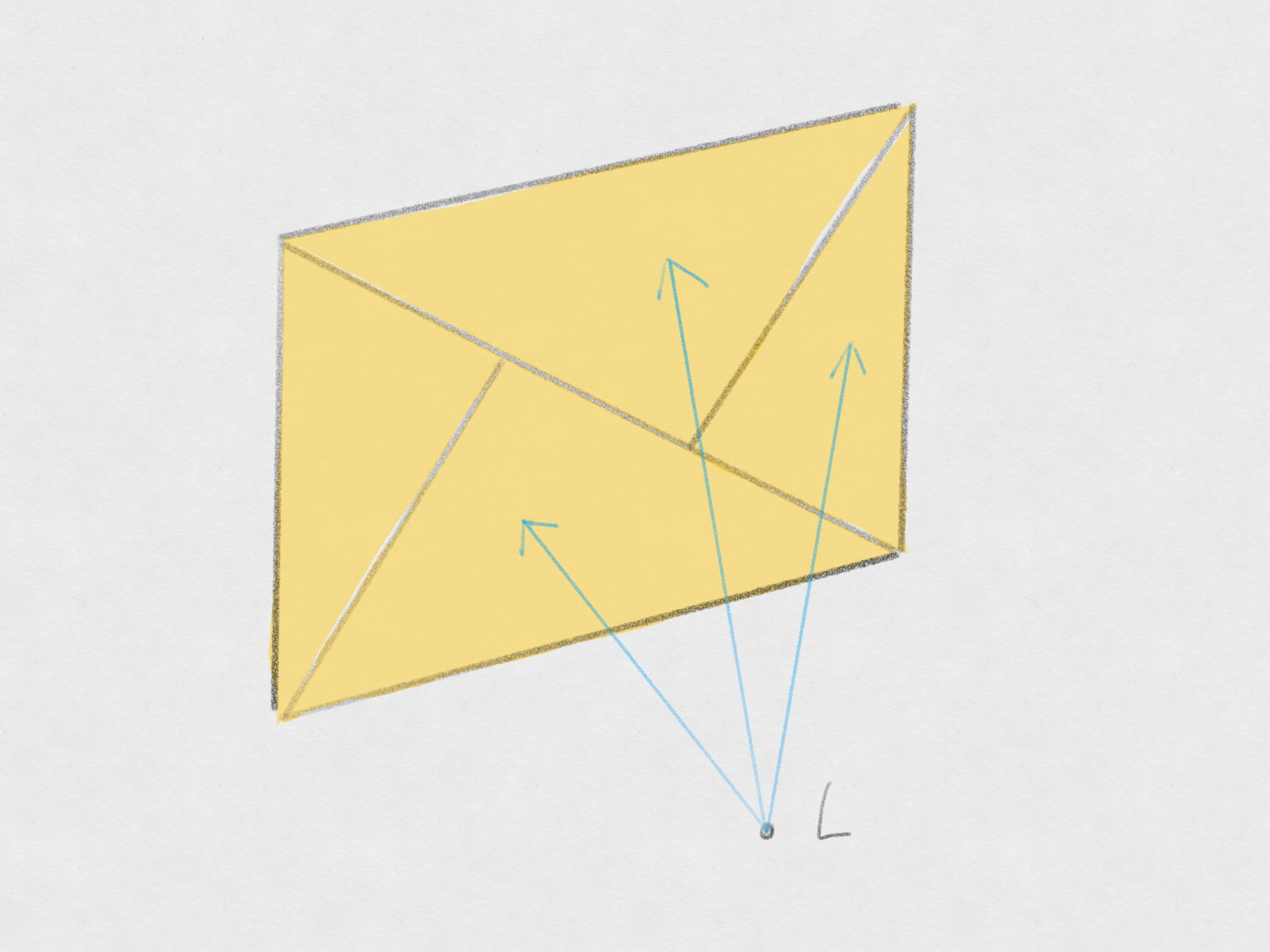
Geometry visible angle
When a triangle is smaller than the sampling density, the raytracing engine is less likely to find it.
지오메트리의 가시 각도(visible angle) 알파는 리스너의 관점에서 지오메트리가 보이는 각도입니다. 주요 레이의 개수에 따라 두 레이 간 평균 각도(감마)는 달라질 수 있습니다. 알파와 감마 간 관계는 오브젝트와의 교차점(반사나 회절)을 찾아낼 수 있는 확률에 영향을 끼칩니다. 만약 감마가 알파보다 작을 경우, 교차점을 찾을 수 있는 확률은 높아집니다. 만약 감마가 알파보다 클 경우, 교차점을 찾을 수 있는 확률은 낮아집니다.


Number of triangles
지오메트리 안의 삼각형 개수는 엔진의 CPU 사용과 직접적으로 연관돼있습니다. 즉, 삼각형 개수가 많을수록 CPU 사용량이 높아집니다. 이는, 해당 오브젝트에 대해 더 많은 교차점 검사가 필요하기 때문입니다. 보통 소리 전달에는 그렇게 상세한 지오메트리가 필요하지 않습니다. 삼각형의 개수를 줄이면 품질을 희생시키지 않고 성능을 높일 수 있습니다.
Geometry shape
다른 것보다 처리하기가 좀 더 까다로운 지오메트리가 있습니다. 일반적으로, 비행기나 상자같은 지오메트리는 처리가 단순하고 소리 전달 측면에서 봤을 때 가장 좋은 결과물을 냅니다. 구체와 원기둥은 오류를 발생시킬 확률이 더 높습니다. 이는 구체나 원기둥의 곡률 때문입니다. 일부 회절 경계를 찾지 못하면 회절 경로를 누락할 수 있습니다. 이 알고리즘은 몇몇 휴리스틱을 시행해 대부분의 이 문제를 해결합니다. 주요 레이 개수를 늘리거나 지오메트리를 단순화하는 방식으로도 이 문제를 해결할 수 있습니다.

Improving Performance
The Performance Monitor can be configured to display many counters related to spatial audio CPU usage. Refer to Performance Monitor Settings for details. The following table provides information you can use to improve spatial audio performance depending on the values of these counters when profiling.
| Symptoms | Possible solutions |
|---|---|
| All spatial audio-related counters are high |
|
| Spatial Audio - Raytracing CPU is high |
|
| Spatial Audio - Path Validation CPU is high |
|
| Spatial Audio - CPU is high (path validation and ray tracing are both involved) |
|
이 페이지가 도움이 되었나요?
작업하는 프로젝트에 대해 알려주세요. 언제든지 도와드릴 준비가 되어 있습니다.
프로젝트를 등록하세요. 아무런 조건이나 의무 사항 없이 빠른 시작을 도와드리겠습니다.
Wwise를 시작해 보세요